Elevate Your Digital
Transformation Journey
RazorSpire propels your brand to new heights through Digital Transformation. We specialise in AI and Marketing.
Strategic Actionable plans
100% Project Delivery Success
Digital Transformation Growth
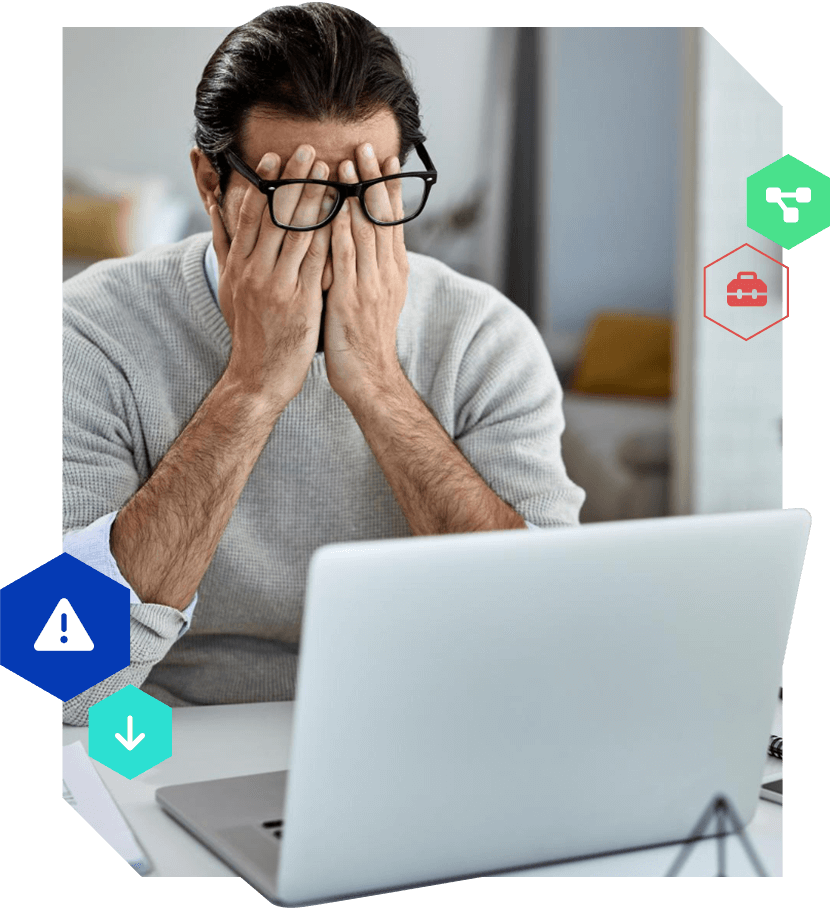

Red Flags In Your Digital Transformation?
3 Ways RazorSpire Can Help
Digital Transformation
We manage and advise on digital transformation projects ranging from overseeing the delivery of a website project up to large scale multi-year project.
AI consultancy
AI is pivotal for your digital transformation. We'll formulate your strategy, define your technology stack and manage the implementation.
Leadership Advisory Services
We work directly with your Leadership team to help navigate your digital transformation journey. We are available on demand as required.
Smart Companies Trust RazorSpire
to help them turn good ideas into great business successes.

Getting More from your digital transformation is easy
Get on the phone with us.
Have a free call with us and if we guarantee we’ll deliver value on this very first call.
1
Assessing your needs
We’ll work with you to assess your needs.
2
Get the help you need
After assessing your needs we’ll work out what resources you need. This could be a combination of internal RazorSpire resources, trusted partners or working with other companies that will need to deliver parts of the solution.
3
Deliver on the project
We have a 100% track record of delivering successful projects and we’ll do the same for you.
4
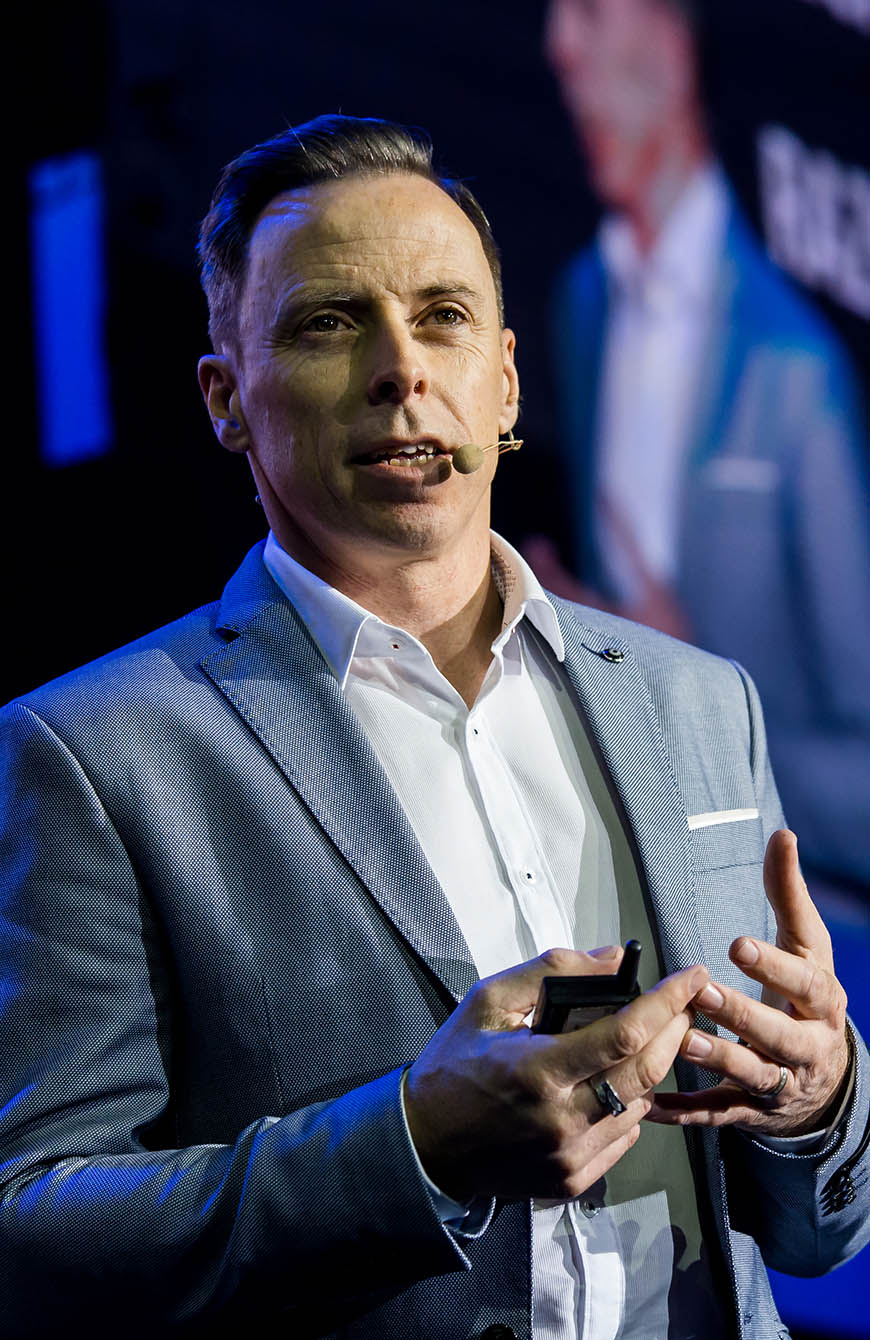

About The Founder
Ian Cleary is a visionary leader in technology, marketing and digital transformation, with over 25 years of global experience and recognition in the field.
AS FEATURED ON






